In the atmosphere there are particles of various sizes such as dusts, aerosols and exhaust gases. Some of these particles spontaneously form in nature, a vomit is a human structure with industrialization. Air pollution is known to cause serious damage to human health. Many industrial production, chemical physical and biological processes are known to cause this pollution. At this point, the importance of air filters arises. Filters are used not only for human health, but also as a means of processes. Standards have been established and laws have been enacted in this regard especially in the US and European countries. (EN - European Norm)
There are 3 main criteria in the selection of air filters;
- Percent Productivity: The efficiency of the filtration is determined according to EN 779 or EN 1822 standard for fine filters and this test determines the filter class. The size and percentage of particles retained by the filter.
- Dust Holding Capacity: The filter with the same efficiency and high dust holding capacity will have a longer life than the other filter.
- Pressure Decrease: With the filter installed in the system, there will be a resistance in the system. The start of the filtration with low pressure differential will bring energy savings.
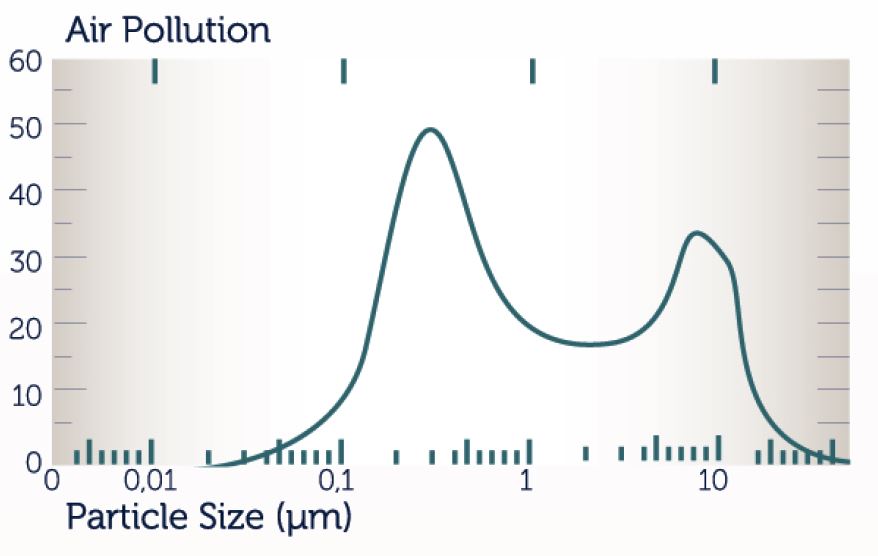
When selecting in air filters, we need to know the particle distribution in the air present in the atmosphere. Secondly, what do we want to filter out of the particles? A coarse particle of size 5-10 micron, which disturbs us in the general particle distribution in the air, a filter of the G3 - G4 class can filter the second peak on the right in the figure below. In this way, 90% of the air we get into the system is cleaned. Particles in the size of 0.2 - 1 micron are not visible to the eye but are large enough to be seen as they intensify. They can be cleaned with F7 - F9 filters. F class filters are 2nd stage filters and used with a G3 - G4 class pre - filter. The chart is the 1 st left on the left. HEPA filters are used to filter out small particles of 0.2 microns. HEPA filters are 3rd or 4th stage filters. There must be 2 or 3 stage filters in the front.
Air Filter Classification
| Filter Class Name | Weight Dust Retention | Productivity % | Initial Dust Retention |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | A < 65 | ||
| G2 | 65 < A < 80 | ||
| G3 | 80 < A < 90 | ||
| G4 | 90 < A | ||
| F5 | 40 < E < 60 | ||
| F6 | 65 < E < 80 | ||
| F7 | 80 < E < 90 | ||
| F8 | 90 < E | ||
| F9 | |||
| H10 | 85 < n | ||
| H11 | 95 < n | ||
| H12 | 99,5 < n | ||
| H13 | 99,95 < n | ||
| H14 | 99,995 | ||
| U15 | 99,9995 | ||
| U16 | 99,9999 | ||
| U17 | 99,9999 | ||
| * 0.4 Percent Mean Percent Value Accepted | |||
| ** MPPS (Most Penetrating Particle Size Percentage) | |||
Particulate Retention Ratios of Filters to EN 779 Test Standards
| Filter Class Name | 0.1 Micron Particle Size | 0.3 Micron Particle Size | 0.5 Micron Particle Size | 1 Micron Particle Size | 3 Micron Particle Size | 5 Micron Particle Size | 10 Micron Particle Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 0-5 | 5-15 | 40-50 | ||||
| G2 | 0-5 | 5-15 | 15-35 | 50-70 | |||
| G3 | 0-5 | 5-15 | 15-35 | -35-70 | 70-85 | ||
| G4 | 0-5 | 5-25 | 25-45 | 30-55 | 60-90 | 85-98 | |
| F5 | 0-10 | 5-15 | 35-50 | 50-70 | 70-90 | 90-99 | >98 |
| F6 | 5-15 | 10-25 | 45-65 | 65-80 | 85-95 | 98-99 | >99 |
| F7 | 25-35 | 45-60 | 70-85 | 85-95 | >98 | >99 | >99 |
| F8 | 35-45 | 65-75 | 80-90 | 95-98 | >99 | >99 | >99 |
| F9 | 45-60 | 75-85 | 90-95 | >98 | >99 | >99 | >99 |
Clean Room Standards
Number of Particles Allowed in 1m³
| Quality Standard | 0,1 µm | 0,2 µm | 0,3 µm | 0,5 µm | 1 µm | 5 µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 1 | 10 | 2 | ||||
| ISO 2 | 100 | 24 | 10 | 4 | ||
| ISO 3 | 1.000 | 237 | 102 | 35 | 8 | |
| ISO 4 | 10.000 | 2.370 | 1.020 | 352 | 83 | |
| ISO 5 | 100.000 | 23.700 | 10.200 | 3.520 | 832 | 29 |
| ISO 6 | 1.000.000 | 237.000 | 102.000 | 35.200 | 8.320 | 293 |
| ISO 7 | 352.000 | 83.200 | 2.930 | |||
| ISO 8 | 3.520.000 | 832.000 | 29.300 | |||
| ISO 9 | 35.200.000 | 8.320.000 | 293.000 |
 TÜRKÇE
TÜRKÇE
 ENGLISH
ENGLISH
 عربى
عربى
 русский
русский
 Español
Español

